Neuroprotective role of a protoberberine alkaloid against aluminum-induced neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55779/nsb15211488Keywords:
Aluminium chloride, BDNF expression, excitotoxicity, neuroprotection, neurotransmitters, neuronal inflammation, palmatineAbstract
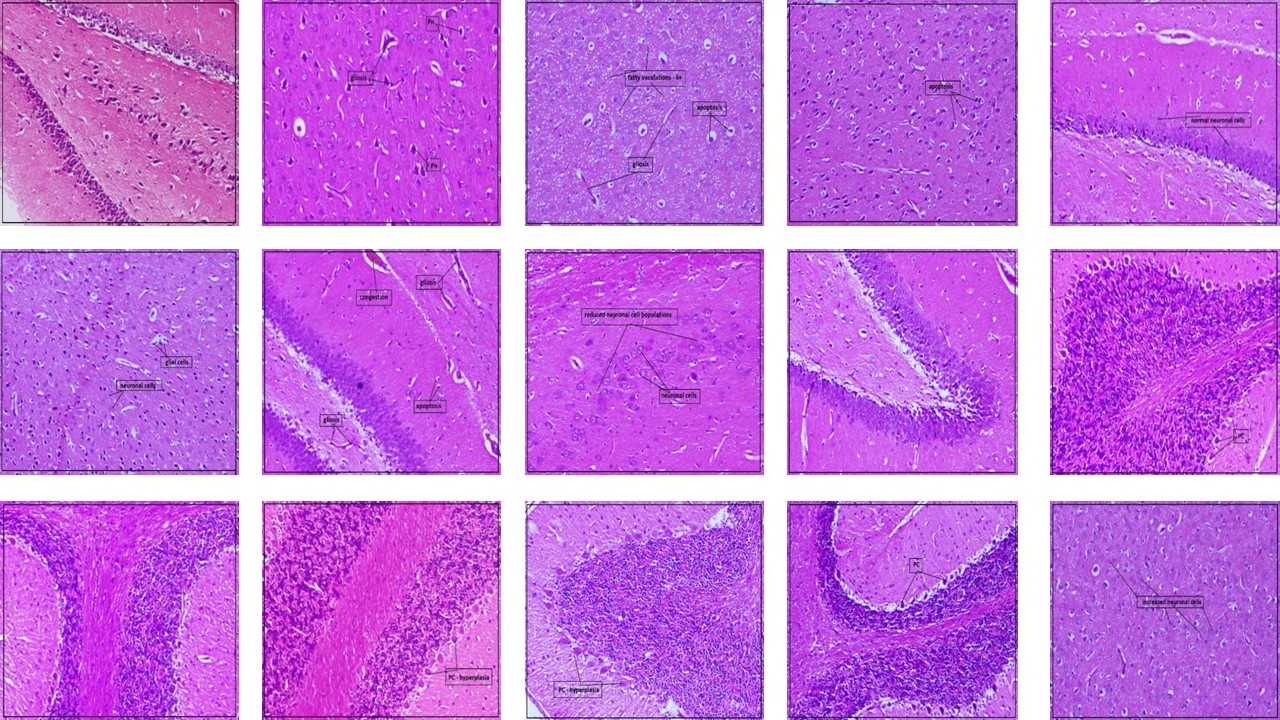
The study was performed to investigate the possible neuroprotective role of palmatine, a protoberberine alkaloid against aluminum-induced aberration in neurotransmitter levels, excitotoxicity, neuronal inflammation, damage, and degeneration. 100 mg/kg of aluminum chloride served as the inducing agent and was administered orally to male Wistar albino rats for 42 consecutive days. Animals were divided into four groups, groups I, II, III, and IV which involve the normal group, the toxic control group receiving aluminum chloride, and two treatment groups administered orally with palmatine at a dose of 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg respectively followed by aluminum chloride. Expression of neuronal inflammatory markers like IL-6 and TNF- α were checked by the ELISA method. Deranged neurotransmitter levels of acetylcholine esterase and glutamate in rat brains were measured to determine the extent of excitotoxicity. The neuroprotective role of palmatine was determined based on histopathological studies and by determining BDNF expression by the immunohistochemistry method in rat brains. Palmatine treatment effectively regulated acetylcholinesterase levels and glutamate levels otherwise elevated by aluminum. It lowered excitotoxic damage induced by aluminum and lowered the degree of expression of inflammatory markers IL-6 and TNF- α. Improved expression of BDNF in palmatine-treated groups is indicative of the neuroprotective potential of palmatine in the restoration of neuroplasticity. Histopathology further confirms the neuroprotective potential of palmatine as the treatment significantly prevented neuronal damage degeneration and loss and restored healthy and viable neurons. The findings of the study confirm the neuroprotective potential of palmatine against aluminum-induced neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity.
Metrics
References
Alghamdi, Ali BS (2018). Possible prophylactic anti-excitotoxic and anti-oxidant effects of virgin coconut oil on aluminium chloride-induced Alzheimer’s in rat models. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience 17(3-4):593-607. https://doi.org/10.3233/jin-180089
Ali H, Dixit S (2013). Extraction optimization of Tinospora cordifolia and assessment of the anticancer activity of its alkaloid palmatine. Scientific World Journal 28:376216. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/376216
Auti ST, Kulkarni YA (2019). Neuroprotective effect of cardamom oil against aluminum induced neurotoxicity in rats. Frontiers in Neurology 10(399):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00399
Barichello T, dos Santos I, Savi GD, Simões LR, Silvestre T, Comim CM, … Quevedo J (2010). TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and cinc-1 levels in rat brain after meningitis induced by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Journal of Neuroimmunology 221(1-2):42-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.02.009
Bhadra K, Kumar GS (2010). Therapeutic potential of nucleic acid-binding isoquinoline alkaloids: Binding aspects and implications for drug design. Medicinal Research Reviews 31(6):821-862. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20202
Cao Z, Wang P, Gao X, Shao B, Zhao S, Li Y (2019). Lycopene attenuates aluminum-induced hippocampal lesions by inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated inflammation and apoptosis in the rat. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 193:143-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.01.017
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961). A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology 7(2):88-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9.
Lima Giacobbo B, Doorduin J, Klein HC, Dierckx RA, Bromberg E, de Vries EF (2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: focus on neuroinflammation. Molecular Neurobiology 56:3295-3312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1283-6
Godbout JP, Johnson RW (2003). Interleukin-6 in the aging brain. Journal of Neuroimmunology 147(1-2):141-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.10.031
Hsieh TJ, Chia YC, Wu YC, Chen CY (2004). Chemical constituents from the stems of Mahonia japonica. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 51(2):443-446. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jccs.200400068
Long J, Song J, Zhong L, Liao Y, Liu L, Li X (2019). Palmatine: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Biochimie 162:176-184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.04.008
Ma WK, Li H, Dong CL (2016). Palmatine from Mahonia bealei attenuates gut tumorigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice via inhibition of inflammatory cytokines. Molecular Medicine Reports 14(1):491-498. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5285
Matsusaka T, Fujikawa K, Nishio Y, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Kishimoto T, Akira S (1993). Transcription factors NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B synergistically activate transcription of the inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 6 and interleukin 8. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 90(21):10193-10197. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.21.10193
Nayak P, Chatterjee AK (2001). Effects of aluminium exposure on brain glutamate and GABA systems: an experimental study in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 39(12):1285-1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-6915(01)00077-1
Paulbabu K, Singh DK, Prashanti P, Padmaja M (2014). Neuroprotective potential and efficacy of neurodegenerative disorders of fruit extract of aeglemarmelos. International Journal Pharmacy and Pharmacological Science 7(1):155-159.
Serra MP, Poddighe L, Boi M, Sanna F, Piludu MA, Corda MG, ... Quartu M (2017). Expression of BDNF and trkB in the hippocampus of a rat genetic model of vulnerability (Roman low‐avoidance) and resistance (Roman high‐avoidance) to stress‐induced depression. Brain and Behavior 7(10):e00861. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.861
Skalny AV, Aschner M, Jiang Y, Gluhcheva YG, Tizabi Y, Lobinski R, Tinkov AA (2021). Molecular mechanisms of aluminum neurotoxicity: Update on adverse effects and therapeutic strategies. In: Advances in Neurotoxicology 5:1-34. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ant.2020.12.001
Tang C, Hong J, Hu C, Huang C, Gao J, Huang J, ... Dong Y (2021). Palmatine protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155%2F2021%2F6660193
Uddin MS, Al Mamun A, Iqbal MA, Islam A, Hossain MF, Khanum S, Rashid M (2016). Analyzing nootropic effect of Phyllanthus reticulatus Poir. on cognitive functions, brain antioxidant enzymes and acetylcholinesterase activity against aluminum-induced Alzheimer’s model in rats: applicable for controlling the risk factors of Alzheimer’s. Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease 5:87-102. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/aad.2016.53007
Zhang YT, Yu YQ, Yan XX, Wang WJ, Tian XT, Wang L, ... Pan GY (2019). Different structures of berberine and five other protoberberine alkaloids that affect P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux capacity. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 40(1):133-142. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0183-7
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ratna BABURAJ, Rajendra SANDUR V, Kuntal DAS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Papers published in Notulae Scientia Biologicae are Open-Access, distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
© Articles by the authors; licensee SMTCT, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright/to retain publishing rights without restriction.
License:
Open Access Journal - the journal offers free, immediate, and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed research and scholarly work, due SMTCT supports to increase the visibility, accessibility and reputation of the researchers, regardless of geography and their budgets. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.













.png)















