Phylogenetic analysis using SCoT markers and chloroplast trnL intron in some Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. (Rosaceae) populations from the Aegean region of Turkey
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55779/nsb14211244Keywords:
Eriobotrya japonica, phylogenetic analysis, SCoT, trnL intronAbstract
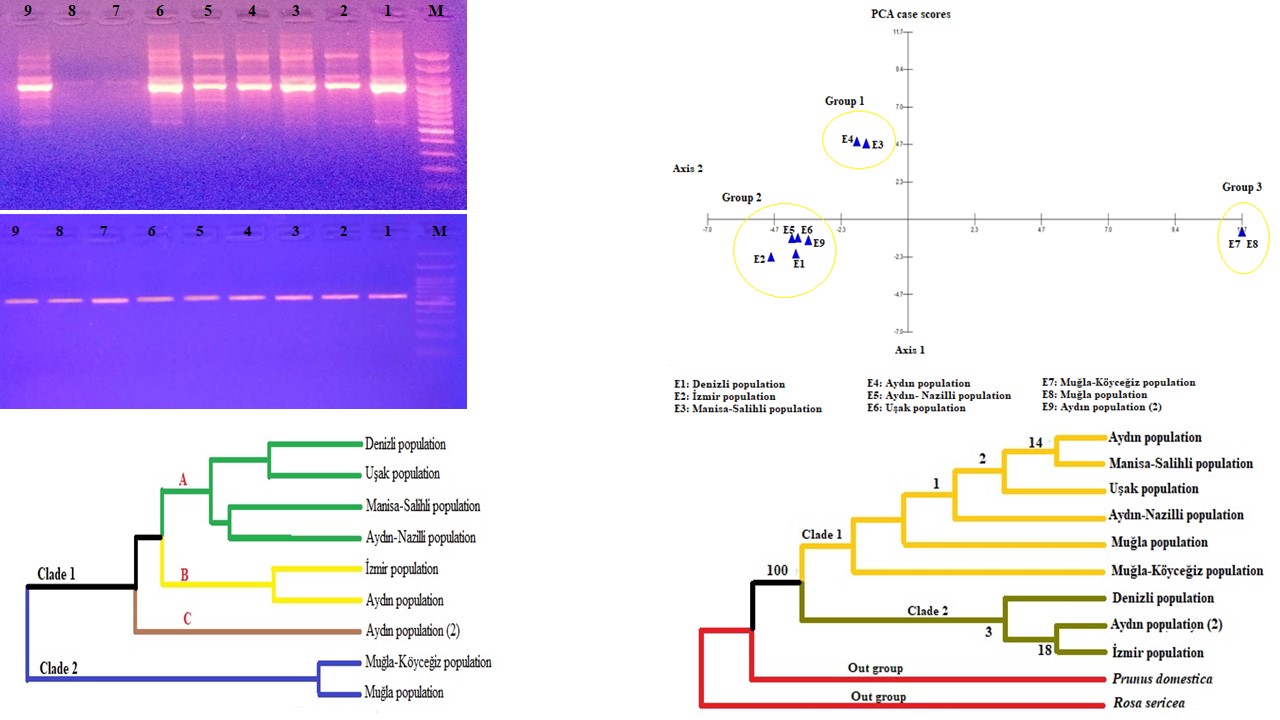
In this study, phylogenetic analyses of some Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. populations based on SCoT marker technique and cpDNA trnL intron sequence analysis were performed. Specimens from the populations were collected from the Aegean region of Turkey and brought to the laboratory for genomic DNA isolation. To determine the phylogenetic analysis of Eriobotrya japonica populations, seven SCoT primers were used. In the SCoT analysis, a total of 54 bands were obtained, 49 of which were polymorphic and 5 were monomorphic. In chloroplast trnL intron region, trnC, trnD primers were used for PCR amplification. Eriobotrya japonica trnL intron sequence lengths were determined to be between 530 and 547 nucleotides. The average nucleotide rate detected as 38.9% for thymine, 18.1% for cytosine, 28.2% for adenine and 14.8% for guanine. Rosaceae family trnL intron sequences belonging to Rhaphiolepis Lindl., Heteromeles M.Roem., Photinia Lindl. Cotoneaster Medik, Sorbus L., Malus Miller, Pyrus L., Prunus L. and Rosa L. were retrieved from NCBI and their phylogenetic relationship with Eriobotrya japonica populations were revealed. As a result of the study, polymorphism rate was determined as 90.74% in SCoT analysis. According to cpDNA trnL intron results, Eriobotrya japonica populations were identified in the same group with Rhaphiolepis indica, a finding supported by past phylogenetic analyzes.
Metrics
References
Agarwal A, Gupta V, Haq SU, Jatav PK, Kothari SL, Kachhwaha S (2019) Assessment of genetic diversity in 29 rose germplasms using SCoT marker. Journal of King Saud University-Science 31(4):780-788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.04.022
Bozhuyuk MR (2022) Morphological and Biochemical Characterization of Wild Sour Cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) Germplasm. Erwerbs-Obstbau 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-022-00656-z
Campbell CS, Evans RC, Morgan DR, Dickinson TA, Arsenault MP (2007) Phylogeny of subtribe Pyrinae (formerly the Maloideae, Rosaceae): limited resolution of a complex evolutionary history. Plant Systematics and Evolution 266(1):119-145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0545-y
Chen X, Li J, Cheng T, Zhang W, Liu Y, Wu P, ... Zhou S (2020a) Molecular systematics of Rosoideae (Rosaceae). Plant Systematics and Evolution 306:1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01629-z
Chen SF, Meng KK, Guo XB, Zhao WY, Liao WB, Fan Q (2020b) A new species of Eriobotrya (Rosaceae) from Yunnan Province, China. PhytoKeys 146:61-69. https://doi.org/10.3897/phytokeys.146.50728
Collard BCY, Mackill DJ (2009) Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 27:86-93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-008-0060-5
Deng Y, Luo Y, He Y, Qin X, Li C, Deng X (2020) Complete chloroplast genome of Michelia shiluensis and a comparative analysis with four Magnoliaceae species. Forests 11(3):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11030267
Drabkova L, Kirschner J, Vlček Č, Pačes V (2004) TrnL–trnF intergenic spacer and trnL intron define major clades within Luzula and Juncus (Juncaceae): importance of structural mutations. Journal of Molecular Evolution 59(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-2598-7
Eroğul D, Oğuz Hİ (2018) Determining the physico-chemical characterstics of the rosehip genotypes grown naturally in Adiyaman Province. Erwerbs-Obstbau 60(3):195-201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-017-0358-2
Ertuş MM, Sabancı CO, Şensoy S (2016) Determination of molecular diversity with ISSR markers in some cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) ecotypes. Journal of Central Research Institute for Field Crops 25:249-254. https://doi.org/10.21566/tarbitderg.280503
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on the phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783-791. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Feng S, Zhu Y, Yu C, Jiao K, Jiang M, Lu J, ... Wang H (2018) Development of species-specific SCAR markers, based on a SCoT analysis, to authenticate Physalis (Solanaceae) species. Frontiers in Genetics 9:192. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00192
Filyushin MA, Boris KV (2017) Polymorphism and the secondary structure of the mitochondrial nad1 gene b/c intron in Malus species and related Rosaceae species. Biology Bulletin 44(4):384-390. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359017040033
Gao YH, Zhu YQ, Tong ZK, Xu ZY, Jiang XF, Huang CH (2014) Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships among genus Lycoris based on start codon targeted (SCoT) marker. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 57:221-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.08.002
Gelotar MJ, Dharajiya DT, Solanki SD, Prajapati NN, Tiwari KK (2019) Genetic diversity analysis and molecular characterization of grain amaranth genotypes using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Bulletin of the National Research Centre 43(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0146-2
Gisbert AD, Martínez-Calvo J, Llácer G, Badenes ML, Romero C (2009) Development of two loquat [Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl.] linkage maps based on AFLPs and SSR markers from different Rosaceae species. Molecular Breeding 23(3):523-538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9253-8
Gupta PK, Varshney RK, Sharma PC, Ramesh B (1999) Molecular markers and their applications in wheat breeding. Plant Breeding 118(5):369-390. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0523.1999.00401.x
Hall TA. (1999) Bioedit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analyses program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium 41:95-98.
He Q, Li XW, Liang GL, Ji K, Guo QG, Yuan WM, … Gao ZS (2011) Genetic diversity and identity of Chinese loquat cultivars/accessions (Eriobotrya japonica) using apple SSR markers. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 29:197-208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0218-9
Idrees M, Lı M, Pathak ML, Qaıser M, Zhang Z, Gao X (2022) A taxonomic revision of the genus Eriobotrya Lindl. (Rosaceae). Pakistan Journal of Botany 54(3):985-1017. http://dx.doi.org/10.30848/PJB2022-3(23)
Idrees M, Wang H, Mitra LP, Zhang ZY, Gao XF (2021a) Phylogenetıc Study of Eriobotrya (Rosaceae) Based on Combined cpDNA psbA-trnH and atpB-rbcL Markers. Journal of Tropical Forest Science 33(3): 343-348.
Idrees M, Pathak ML, Memon NH, Khan S, Zhang ZY, Gao XF (2021b) Morphologıcal and morphometrıc analysıs of genus Eriobotrya Lındl. (Rosaceae). JAPS: Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences 31(4).
Karanjalker G, Begane N (2016. Breeding perennial fruit crops for quality improvement. Erwerbs-Obstbau 58(2):119-126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-015-0264-4
Kottaimuthu R, Basu MJ (2021) A new replacement name for Eriobotrya integrifolia Aver.(Rosaceae). Kew Bulletin 76:859. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12225-021-09975-y
Kovach WL (2007) MVSP-A MultiVariate Statistical Package for Windows, ver. 3.1. Kovach Computing Services, Pentraeth, Wales, U.K.
Li F, Xie X, Huang R, Tian E, Li C, Chao Z (2021) Chloroplast genome sequencing based on genome skimming for identification of Eriobotryae Folium. BMC Biotechnology 21(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-021-00728-0
Li P, Lin S, Yang X, Hu G, Jiang Y (2009) Molecular phylogeny of Eriobotrya Lindl. (Loquat) inferred from internal transcribed spacer sequences of nuclear ribosome. Pakistan Journal of Botany 41(1):185-193.
Li P, Yang X H, Hu GB, Lin SQ (2010) A preliminary phylogenetic study of Eriobotrya based on cpDNA rbcL and trnL-F sequences. In: III International Symposium on Loquat 887:79-83.
Lin L, Junqiang L, Zong H, Wang Y (2021) Effect of antibiotics on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation from anther derived embryos of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. cv. ‘Dawuxing’. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 96(2):172-182. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2020.1814876
Liu BB, Liu GN, Hong DY, Wen J (2020) Eriobotrya belongs to Rhaphiolepis (Maleae, Rosaceae): Evidence from chloroplast genome and nuclear ribosomal DNA data. Frontiers in Plant Science 10:1731. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01731
Özdemir B, Altıntaş S, Özrenk K, Çelik F (2020) Genetic characterization of edible fig (Ficus carica L.) genotypes grown in Siirt region based on trnL-F region. Journal of Biological & Environmental Sciences 14(42):137-142
Rayan WA, Osman SA (2019) Phylogenetic relationships of some Egyptian soybean cultivars (Glycine max L.) using SCoT marker and protein pattern. Bulletin of the National Research Centre 43(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0197-4
Sagdic O, Polat B, Yetim H (2022) Bioactivities of Some Wild Fruits Grown in Turkey. Erwerbs-Obstbau 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10341-021-00631-0
Sarra C, Soumaya R-C, Zined M, Khaled S, Noureddine C, Khaled C (2015) Chloroplast DNA analysis of Tunisian pistachio (Pistacia vera L.): sequence variations of the intron trnL (UAA). Scientia Horticulturae 191:57-64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.04.037
Sevindik E, Okan K, Efe F (2020) Analysis of Genetic Diversity Between Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. (Rosaceae) Populations Growing in the Aegean Region of Turkey. Bulletin UASVM Horticulture 77(2):71-75. http://dx.doi.org/10.15835/buasvmcn-hort:2020.0012
Shen L, Guan Q, Amin A, Zhu W, Li M, Li X, ... Tian J (2016) Complete plastid genome of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl and comparative analysis in Rosaceae. SpringerPlus 5(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3702-3
Singh SK, Chhajer S, Pathak R, Bhatt RK, Kalia RK (2017) Genetic diversity of Indian jujube cultivars using SCoT, ISSR, and rDNA markers. Tree Genetics & Genomes 13(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1092-x
Soriano JM, Romero C, Vilanova S, Llácer G, Badenes ML (2005) Genetic diversity of loquat germplasm (Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb) Lindl) assessed by SSR markers. Genome 48(1):108-114. https://doi.org/10.1139/g04-101
Sun J, Shi S, Li J, Yu J, Wang L, Yang X, ... Zhou S (2018) Phylogeny of Maleae (Rosaceae) based on multiple chloroplast regions: implications to genera circumscription. BioMed Research International 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7627191
Swofford DL (2001) PAUP. phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods), version 4.0b10. for 32-bit microsoft windows Sinaeur Associates, Sunderland
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Molecular Biology 17:1105-1109. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037152
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30:2725-2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tyagi S, Jung JA, Kim JS, Won SY (2020) A comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of three Chrysanthemum boreale strains. PeerJ 8:e9448. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9448
Xinaghui Y, Pıng L, Zhike Z, Shunquan L, Guibin H, Xiaolong H (2012) A preliminarily phylogeny study of the Eriobotrya based on the nrDNA Adh sequences. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj Napoca 40:233-237. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha4027997
Wang YQ, Fu Y, Yang Q, Deng QX, Lu XL, Luo, Yan J (2010) Analysis of a germplasm collection of loquat using ISSR markers. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology 85(2):113-118. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2010.11512640
Yang X, Liu C, Lin S (2009) Genetic relationships in Eriobotrya species as revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers. Scientia Horticulturae 122(2):264-268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2009.04.012
Yijie Z, Jiangbo, Xiaohong Z, Weishu S, Hang L (2010) ISSR Molecular Identification of Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. ‘Dong Huzao[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops 31(1):72-76.
Yue Q, Zhang C, Wang Q, Wang W, Wang J, Wu Y (2019) Analysis on genetic diversity of 51 Grape germplasm resources. Ciência Rural 49. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr2090247
Zhang J, Xie W, Wang Y, Zhao X (2015) Potential of start codon targeted (SCoT) markers to estimate genetic diversity and relationships among Chinese Elymus sibiricus accessions. Molecules 20(4):5987-6001. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20045987
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Papers published in Notulae Scientia Biologicae are Open-Access, distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
© Articles by the authors; licensee SMTCT, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright/to retain publishing rights without restriction.
License:
Open Access Journal - the journal offers free, immediate, and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed research and scholarly work, due SMTCT supports to increase the visibility, accessibility and reputation of the researchers, regardless of geography and their budgets. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.













.png)















