Subacute hepatotoxicity of alkaloids extracts of Peganum harmala L. seeds in Wistar albino rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55779/nsb14211211Keywords:
alkaloids, hepatotoxicity, liver histology, Peganum harmala, serum biochemical, Wistar ratsAbstract
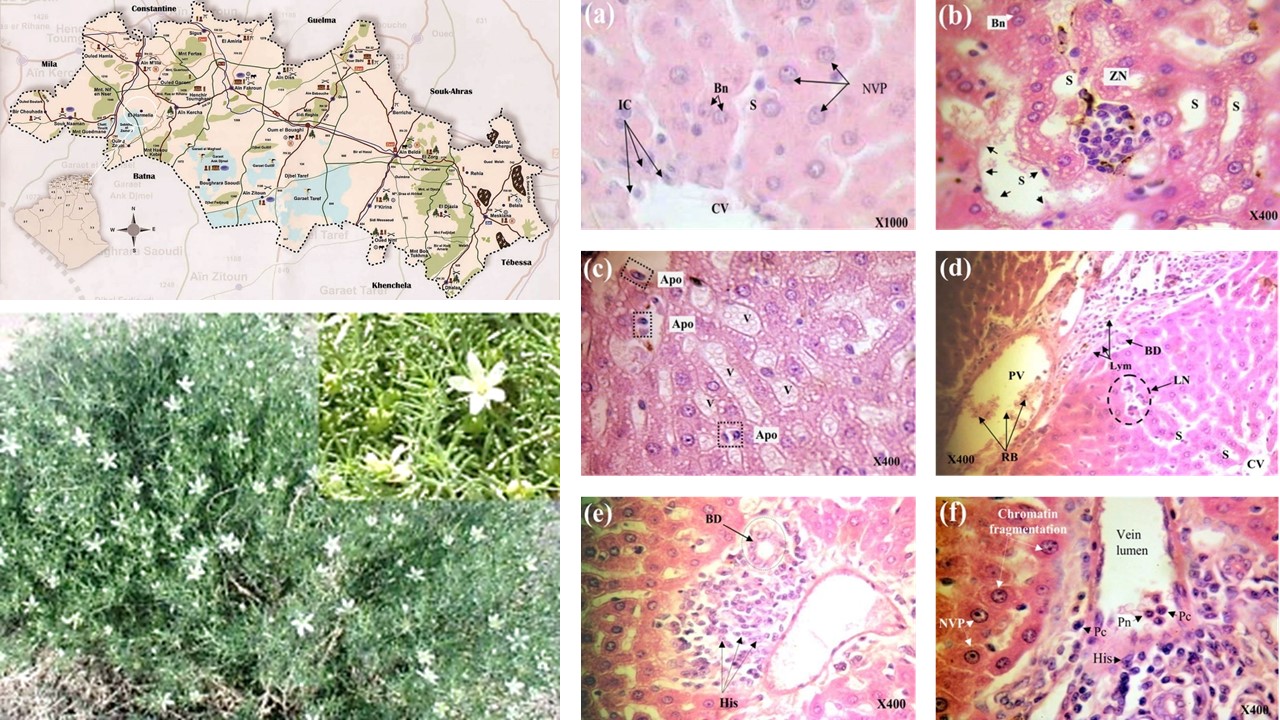
Peganum harmala L. is a medicinal herbal plant widely used in Algerian traditional medicine. Some reports indicated the toxicity of this plant. In this context, the present study focused on investigate the subacute toxicity of alkaloids extract of P. harmala seeds on histo-function of the liver in rats. Sixteen adult Wistar albino rats were divided equally into four groups, and treated intraperitoneally for 30 days. Group I served as control, received water. Group II, group III, and Group IV received daily a single dose of 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg b.w of crude alkaloids of P. harmala respectively. Blood was collected for the determination of ALT, AST and ALP. Sections of the liver were prepared for histological studies. The results showed a significant decrease in body weights of animals and a significant increase in relative weights of liver in groups III and IV. Treated groups with alkaloids extract of seeds showed a significant increase in the concentration of ALT, AST, and ALP enzymes as compared to control group. These findings were supported with histopathological examination of liver of treated rats. Liver of groups III and IV suffered from severe tissue damage, which included inflammation, cell necrosis, and increase in the volume of some hepatocytes. Some cells contained more than one nucleus and cytoplasm contained micro vacuoles, indicating the onset of steatosis. In conclusion, these biochemical and pathological changes indicate dysfunction with hepatocyte damage. Therefore, the seeds of P. harmala plant must be used in herbal medicine with caution to avoid toxicity to the organism.
Metrics
References
Abderrahman SM, Soliman S, Mohammad MG (2018). Genotoxic effects of Peganum harmala L. in relation to traditional use. Journal od Pharmacognosy and Phytotherapy 10(9):167-173. https://doi.org/10.5897/JPP2018.0493
Akhtar MF, Raza SA, Saleem A, Hamid I, Ashraf Baig MMF, Sharif A, … Saleem U (2022). Appraisal of anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory potential of folkloric medicinal plant Peganum harmala. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets 22(1):49-63. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530321666210208211310
AL-Jborrey MH, Al-Shahwany AW (2017). Histopathological effect of (Peganum harmala) alcoholic extract of seeds on liver and kidney in mice. Biomedicine and Biotechnology 5(1):1-5. https://doi.org/10.12691/bb-5-1-1
Al-Saikhan FI, Ansari MN (2016). Evaluation of the diuretic and urinary electrolyte effects of methanolic extract of Peganum harmala L. in Wistar albino rats. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 23(6):749-753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.025
Balbaa SI, Hilal S H, Zaki AY (1981). Medicinal plant constituent. Egyptain – Dar- El- Kotob, pp, 424-437.
Benbott A, Mahdi D, Derouiche K, Karouche S, Zellagui A (2018a). Nephrotoxicity of crude alkaloids extract of Peganum Harmala seeds in rats. World Journal of Environmental Biosciences 7(3):63-66.
Benbott A, Mahdi D, Zellagui A, Moumen Y, Mosbah C (2018b). Effect of alkaloids extract of Peganum harmala seeds on histo- function of rat’s testes. Journal of New Technology and Materials (JNTM) 8(2):70-76.
Berdai MA, Labib S, Harandou M (2014). Peganum harmala L. Intoxication in a pregnant woman. Case Reports in Emergency Medicine 1:1-4. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/783236.
Betti HA, Stein AC, Dallegrave E, Barth Wouters AT, Negrão Watanabe TT, Driemeier D, … Kuze Rates MS (2012). Acute and repeated-doses (28 days) toxicity study of Hypericum polyanthemum Klotzsch ex Reichardt (Guttiferare) in mice. Food and Chemical Toxicology 50(7):2349-2355. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.fct.2012.04.012
Boeira JM, Viana AF, Picada JN, Henriques JA (2002). Genotoxic and recombi-nogenic activities of the two beta-carboline alkaloids harman and harmine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 50:39-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00294-9
Bournine L, Bensalem S, Fatmi S, Bedjou F, Mathieu V, Iguer-Ouada M, … Duez P (2017). Evaluation of the cytotoxic and cytostatic activities of alkaloid extracts from different parts of Peganum harmala L. (Zygophyllaceae). European Journal of Integrative Medicine 9:91-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2016.10.002
Clark JD, Gebhart GF, Janet C, Gonder JC, Michale E, Keeling ME, Kohn DF (1997). The 1996 guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. ILAR Journal 38(1):41-48. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.38.1.41
Diwan SY (2013). Effect of Peganum harmala methanol extract on liver and kidney of mice administered MTX drug. Journal of Al-Nahrain University 16 (4):161-166.
El Gendy MA, El-Kadi AO (2009). Peganum harmala L. differentially modulates cytochrome P450 gene expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Drug Metabolism Letters 3(4):212-216. https://doi.org/10.2174/187231209790218163
Gebrezgi EM, Hiben MG, Kidanu KG, Tsegay AT (2020). Subacute hepatotoxicity of extracts of Senna occidentalis seeds in Swiss albino mice. Journal of Toxicology 2020:8843044. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8843044
Ghizlane EA, Manal M, Ines HA, Soufiane D, Moussa L, Houssam B, Brahim H (2021). Fatal poisoning of pregnant women by Peganum harmala L.: A case reports. Annals of Medicine and Surgery 68(2021):102649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102649
Gonzalo JD (2015). Toxicosis by plant alkaloids in humans and animals in Colombia. Toxins 7(12):5408-5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124892
Hammiche V, Merad R, Azzouz M (2013). Plantes toxiques à usage médicinal du pourtour méditerranéen [Poisonous plants for medicinal use around the Mediterranean]. Paris, Springer.
Herraiz T, González D, Ancín-Azpilicueta C, Arán VJ, Guillén H (2010). Beta-Carboline alkaloids in Peganum harmala and inhibition of human monoamine oxidase (MAO). Food and Chemical Toxicology 48(3):839-845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.12.019
Herraiz T, Guillen H, Aran VJ, Salgado A (2017). Identification, occurrence and activity of quinazoline alkaloids in Peganum harmala. Food and Chemical Toxicology 103:261 269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.03.010
Kalhor N, Eini AM, Sharifi Y, Fazaely H, Far MA (2015). Effect of Peganum harmala L. on lipid metabolism and changes HMGcoA reductase in Hypercholesterolemia-induced male Wistar rat. The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences (ICH & HPSY) 5:3-11. http://dx.doi.org/10.15405/epsbs.2015.07.2
Komeili G, Hashemi M, Bameri-Niafar M (2016). Evaluation of antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of Peganum harmala seeds in diabetic rats. Cholesterol 1:1-6.https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7389864
Lamchouri F (2014). Antitumor properties and toxicity effects of Peganum harmala L. (Zygophyllaceae). Plant Science Today 1(4):192-195. http://dx.doi.org/10.14719/pst.2014.1.4.71
Madah M, Haddad S, Khazeml M (2020). Evaluation of the effect of Peganum harmala extracts on the in vitro viability of Leishmania tropica promastigotes in comparison to Glucantime. Journal of Parasitic Diseases 44(4):858-863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-020-01232-6
Mahmoudian M, Jalilpour H, Salehian P (2002). Toxicity of Peganum harmala: Review and a case report. Iranian Journal of Pharmacolology & Therapeutics 1:1-4.
Maronpot RR, Yoshizawa K, Nyska K, Harada T, Flake G, Mueller G, … Ward MJ (2010). Hepatic Enzyme Induction: Histopathology. Toxicologic Pathology 38:776-795. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623310373778
Mohamed AHS, AL- Jammali SMJ, Naki ZJ (2013). Effect of repeated administration of Peganum harmala alcoholic extract on the liver and kidney in Albino mice: A histo-pathological study. Journal of Scientific & Innovative Research 2(3):585-597.
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Barraud H, Petit-Laurent F, Ancel D, Watelet J, Chone L, … Bronowicki JP (2004). Hépatotoxicité de la phytothérapie: données cliniques, biologiques, histologiques et mécanismes en cause pour quelques exemples caractéristiques [Hepatotoxicity of herbalmedicine: clinical, biological, histological data and mechanismsinvolved for somecharacteristic examples]. Gastroentérologie Clinique et Biologique 28:540-550. https://doi.org/GCB-6-2004-28-6-7-C1-0399-8320-101019-ART3
Sahaphong S, Toskulkao C, Glinsukon T (1992). Enhanced hepatotoxicity of aflatoxin B1 in the rat by ethanol: ultrastructural changes. Toxicology Letters 61(1):89-98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4274(92)90067-t
Sallah N, Amamou M, Jerbi Z, Ben Salah F, Yacoub M (1986). Un cas de surdosage en Peganum harmala L. [A case of Peganum harmala L. overdose]. Journal de Toxicologie Clinique et Expérimentale 6(5):319-322.
Rasekh HR, Nazari P, Kamli-Nejad M, Hosseinzadeh L (2008). Acute and subchronic oral toxicity of Galega officinalis in rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 116(1):21-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.030
Yan F, Wang Q, Xu C, Cao M, Zhou X, Wang T, Yu C, Jing F, Chen W, Gao L, Zhao J (2014). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor a activation induces hepatic steatosis, suggesting an adverse effect. PLoS One 9(6):e99245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099245
Zhao F, Xie P, Jiang J, Zhang L, An W, Zhan1 Y (2014). The effect and mechanism of tamoxifen-induced hepatocyte steatosis in vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15(3):4019-4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15034019
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Papers published in Notulae Scientia Biologicae are Open-Access, distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
© Articles by the authors; licensee SMTCT, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright/to retain publishing rights without restriction.
License:
Open Access Journal - the journal offers free, immediate, and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed research and scholarly work, due SMTCT supports to increase the visibility, accessibility and reputation of the researchers, regardless of geography and their budgets. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.













.png)















