Molecular docking and pharmacokinetic screening of eucalyptol (1,8 cineole) from eucalyptus essential oil against SARS-CoV-2
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb12210711Keywords:
COVID-19; eucalyptus; screeningAbstract
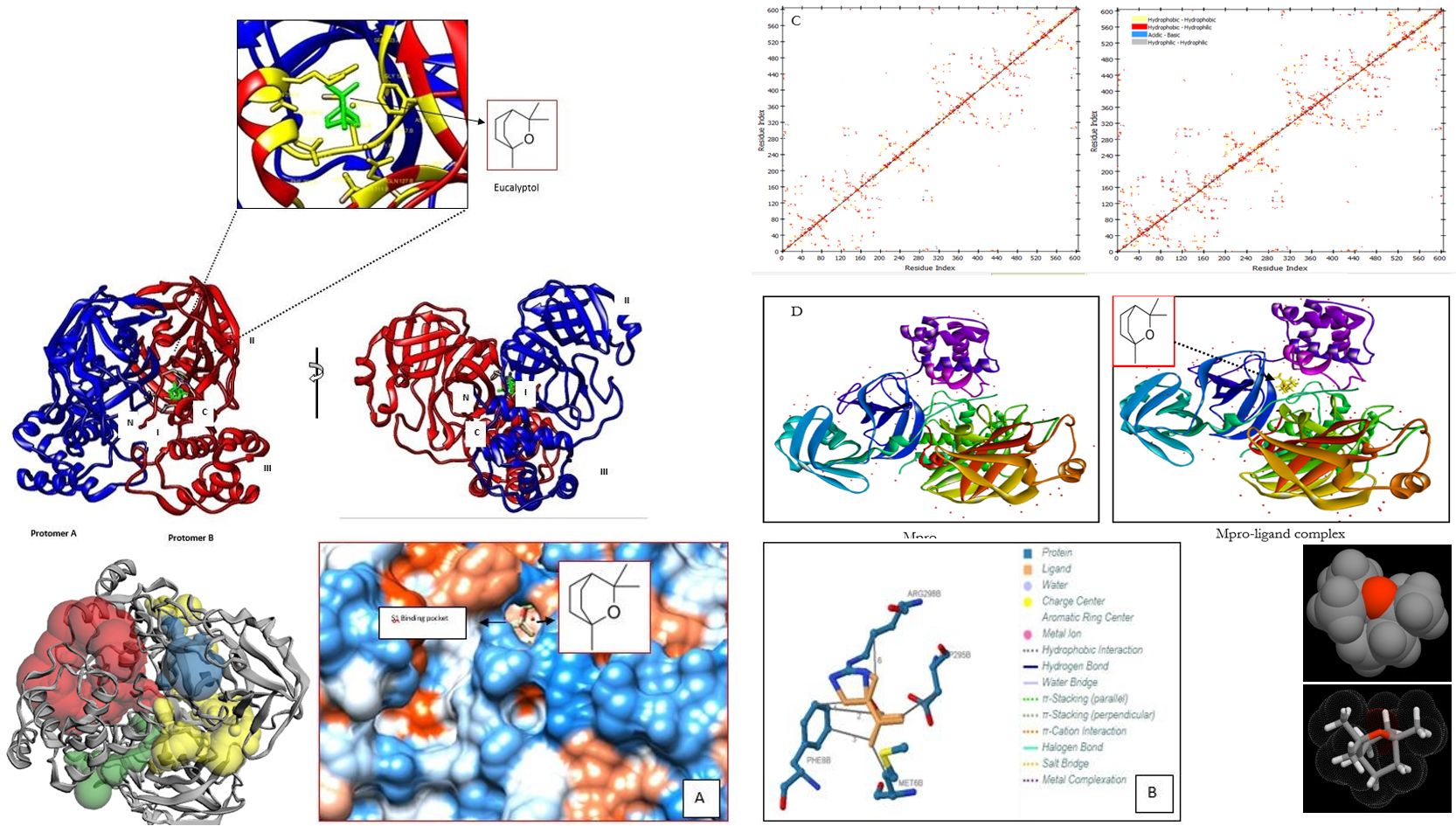
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), member of corona virus family, is a positive single stranded RNA virus. Due to lack of drugs it is spreading its tentacles across the world. Being associated with cough, fever, and respiratory distress, this disease caused more than 15% mortality worldwide. Mpro/3CLpro has recently been regarded as a suitable target for drug design due to its vital role in virus replication. The current study focused on the inhibitory activity of eucalyptol (1,8 cineole), an essential oil component from eucalyptus oil, against Mpro/3CLprofrom SARS-CoV-2. Till date there is no work is undertaken on in-silico analysis of this compound against Mpro/3CLproof SARS-CoV-2. Molecular docking studies were conducted by using 1-click dock tool and Patchdock analysis. In-silico absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET) profile were also studied. The calculated parameters such as docking score indicated effective binding of eucalyptol to COVID-19 Mpro protein. Active site prediction revealed the involvement of active site residues in ligand binding. Interactions results indicated that, Mpro/3CLpro/eucalyptol complexes forms hydrophobic interactions. ADMET studies provided guidelines and mechanistic scope for identification of potent anti-COVID 19 drug. Therefore, eucalyptol may represent potential herbal treatment to act as COVID-19 Mpro/3CLproinhibitor, a finding which must be validated in vivo.
Metrics
References
Goodger JQD, Seneratne SL, Nicolle D, Woodrow IE (2016). Foliar essential oil glands of eucalyptus subgenus Eucalyptus (Myrtaceae) are a rich source of flavonoids and related non-volatile constituents. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0151432. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151432
Im K, Kim J, Min H (2015). Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean red ginseng against viral infection. Journal of Ginseng Research 40(4):309-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002
Lipinski CA (2004). Lead- and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 1:337-341.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007
Liu X, Wang XJ (2020). Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically 13 of 14 approved medicine. Journal of Genetics and Genomics 47(2):119-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2020.02.001.
Lu H (2020). Drug treatment options for the 2019-new coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Bioscience Trends 14(1):69-71. https://doi.org/10.5582/bst.2020.01020
Rodríguez-Morales P, Alfonso J, MacGregor K, Kanagarajah S, Dipti P (2020). Going global - travel and the 2019 novel coronavirus. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 33:101578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101578
Tan J, Verschueren KHG, Anand K, Shen J, Yang M, Xu Y, … Hilgenfeld R (2005). pH-dependent conformational flexibility of the SARS-CoV main proteinase (Mpro) dimer: Molecular dynamics simulations and multiple X-ray structure analyses. Journal of Molecular Biology 354(1):25-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.012
Sharma AD, Kaur I (2020). Molecular docking studies on jensenone from eucalyptus essential oil as a potential inhibitor of COVID 19 corona virus infection. Research and Reviews in Biotechnology and Biosciences 1:59-66.
Shukla A, Sharma P, Prakash O, Singh M, Kalani K, Khan F, … Srivastava SK (2014). QSAR and docking studies on Capsazepine derivatives for immunomodulatory and anti- inflammatory activity. PLoS One 9(7):e100797. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100797
Yang L, Wen KS, Ruan X, Zhao YX, Wei F, Wang Q (2018). Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 23:1-26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040762
Zakaryan H, Arabyan E, Oo A, Zandi K (2017). Flavonoids: promising natural compounds against viral infections. Archives of Virology 162:2539-2551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3417-y
Zhang L, Lin D, Sun X, Curth U, Drosten C, Sauerhering L, … Hilgenfeld R (2020) Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved -ketoamide inhibitors. Science 368(6489):409-412. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abb3405
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Papers published in Notulae Scientia Biologicae are Open-Access, distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
© Articles by the authors; licensee SMTCT, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. The journal allows the author(s) to hold the copyright/to retain publishing rights without restriction.
License:
Open Access Journal - the journal offers free, immediate, and unrestricted access to peer-reviewed research and scholarly work, due SMTCT supports to increase the visibility, accessibility and reputation of the researchers, regardless of geography and their budgets. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author.













.png)















